0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, in Fleboflex Luer container
Partners in secure solutions

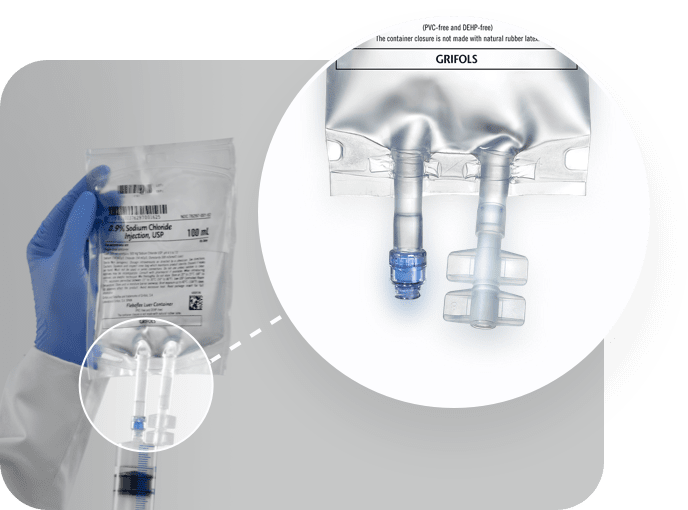
Delivering an innovative, safe, and convenient IV solution
Fleboflex® Luer is an innovative container that combines safety and convenience when preparing and administering IV drugs
- Made of polypropylene: free of PVC, plasticizers, adhesives, and latex
- With a needle-free system that avoids the risk of accidental punctures
- Comes partially filled: large additive volume
Fleboflex® Luer means safety
Fleboflex® Luer means convenience
Max. additive volume in mL up to a pressure of 50 mL bar
- 50/100 mL
-
136
- 100/250 mL
-
289
- 250/500 mL
-
422
- 500/1000 mL
-
639
Maximum removable volume (mL)
- 50/100 mL
-
187
- 100/250 mL
-
394
- 250/500 mL
-
677
- 500/1000 mL
-
1139
Residual volume (mL)
- 50/100 mL
-
0.3-1.8
- 100/250 mL
-
0.3-1.5
- 250/500 mL
-
0.2-1.9
- 500/1000 mL
-
0.2-2.6
Air volume (mL)
- 50/100 mL
-
4-5
- 100/250 mL
-
5-20
- 250/500 mL
-
12-30
- 500/1000 mL
-
15-30
| Fleboflex® Luer | 50/100 mL | 100/250 mL | 250/500 mL | 500/1000 mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Max. additive volume in mL up to a pressure of 50 mL bar |
136 |
289 |
422 |
639 |
|
Maximum removable volume (mL) |
187 |
394 |
677 |
1139 |
|
Residual volume (mL) |
0.3-1.8 |
0.3-1.5 |
0.2-1.9 |
0.2-2.6 |
|
Air volume (mL) |
4-5 |
5-20 |
12-30 |
15-30 |
Compatibility Studies1
1. Compatibility - Internal studies elaborated by Grifols (v1.0) - all document shares internal studies elaborated by grifols (p.1)
Fleboflex® Luer has drug-container compatibility studies with a select number of drugs*
Bleomycin sulfate
- Size
-
0.15 U/mL in 0.9% SC
- 25 °C (77 °F)†
-
7 days
Carboplatin
- Size
-
0.5 mg/mL in 0.9% SC
- 25 °C (77 °F)†
-
7 days
Cisplatin
- Size
-
0.5 mg/mL in 0.9% SC
- 25 °C (77 °F)†
-
7 days
Cytarabine
- Size
-
13 mg/mL in 0.9% SC
- 25 °C (77 °F)†
-
1 day
Dacarbazine*‡§
- Size
-
3.4 mg/mL in 0.9% SC
- 25 °C (77 °F)†
-
7 days
Docetaxel
- Size
-
0.3 mg/mL in 0.9% SC
- 25 °C (77 °F)†
-
7 days
Etoposide
- Size
-
0.3 mg/mL in 0.9% SC
- 25 °C (77 °F)†
-
7 days
Epirubicin
- Size
-
2 mg/mL in 0.9% SC
- 25 °C (77 °F)†
-
7 days
Fludarabine
- Size
-
6 mg/mL in 0.9% SC
- 25 °C (77 °F)†
-
7 days
Gemcitabine
- Size
-
4 mg/mL in 0.9% SC
- 25 °C (77 °F)†
-
7 days
Idarubicin
- Size
-
1 mg/mL in 0.9% SC
- 25 °C (77 °F)†
-
7 days
Ifosfamide
- Size
-
1 mg/mL in SC
- 25 °C (77 °F)†
-
7 days
Irinotecan
- Size
-
2.8 mg/mL in SC
- 25 °C (77 °F)†
-
7 days
Methotrexate
- Size
-
1 mg/mL in 0.9% SC
- 25 °C (77 °F)†
-
7 days
Mitoxantrone
- Size
-
0.2 mg/mL in 0.9% SC
- 25 °C (77 °F)†
-
7 days
Oxaliplatin
- Size
-
0.6 mg/mL in 0.9% SC
- 25 °C (77 °F)†
-
7 days
Paclitaxel
- Size
-
0.3 mg/mL in 0.9% SC
- 25 °C (77 °F)†
-
7 days
Vinblastine
- Size
-
0.2 mg/mL in 0.9% SC
- 25 °C (77 °F)†
-
7 days
Vincristine
- Size
-
0.04 mg/mL in 0.9% SC
- 25 °C (77 °F)†
-
7 days
Vinorelbine
- Size
-
1 mg/mL in 0.9% SC
- 25 °C (77 °F)†
-
7 days
| Drug | Size | 25 °C (77 °F)† |
|---|---|---|
|
Bleomycin sulfate |
0.15 U/mL in 0.9% SC |
7 days |
|
Carboplatin |
0.5 mg/mL in 0.9% SC |
7 days |
|
Cisplatin |
0.5 mg/mL in 0.9% SC |
7 days |
|
Cytarabine |
13 mg/mL in 0.9% SC |
1 day |
|
Dacarbazine*ठ|
3.4 mg/mL in 0.9% SC |
7 days |
|
Docetaxel |
0.3 mg/mL in 0.9% SC |
7 days |
|
Etoposide |
0.3 mg/mL in 0.9% SC |
7 days |
|
Epirubicin |
2 mg/mL in 0.9% SC |
7 days |
|
Fludarabine |
6 mg/mL in 0.9% SC |
7 days |
|
Gemcitabine |
4 mg/mL in 0.9% SC |
7 days |
|
Idarubicin |
1 mg/mL in 0.9% SC |
7 days |
|
Ifosfamide |
1 mg/mL in SC |
7 days |
|
Irinotecan |
2.8 mg/mL in SC |
7 days |
|
Methotrexate |
1 mg/mL in 0.9% SC |
7 days |
|
Mitoxantrone |
0.2 mg/mL in 0.9% SC |
7 days |
|
Oxaliplatin |
0.6 mg/mL in 0.9% SC |
7 days |
|
Paclitaxel |
0.3 mg/mL in 0.9% SC |
7 days |
|
Vinblastine |
0.2 mg/mL in 0.9% SC |
7 days |
|
Vincristine |
0.04 mg/mL in 0.9% SC |
7 days |
|
Vinorelbine |
1 mg/mL in 0.9% SC |
7 days |
Bag features
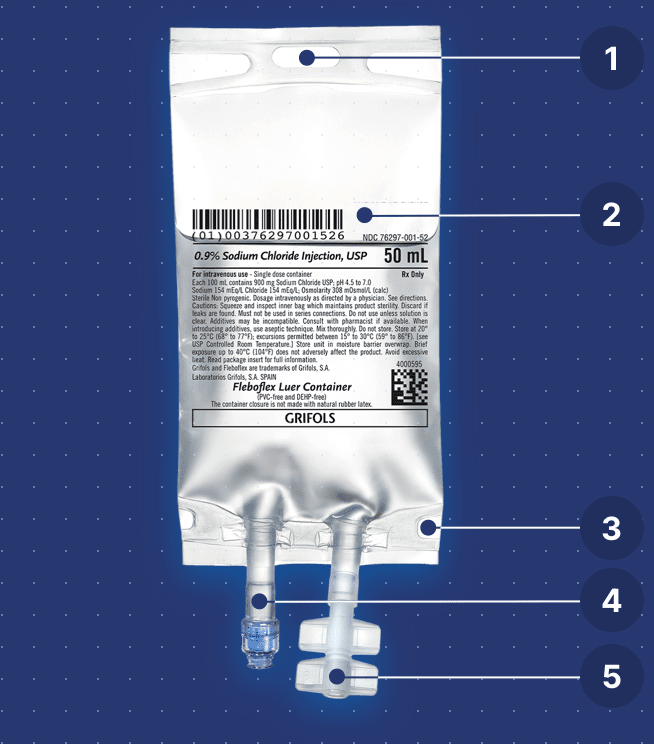
Designed for safe and easy handling
Integrated eyelet support for easy and safe handling of the container during the infusion.
Product information
- Inclusion of the National Drug Code
- Inclusion of lot and expiration date
- Sequential number
Highly compatible material
The solution is only in contact with polypropylene. Both the multilayer film and the inner membranes of the medication and outlet ports contain only polypropylene.
Polypropylene can be sterilized at a higher temperature because it resists heat better than other olefins.
High sealing resistance
High resistance to pressure cuffs.
Injection/extraction port
Luer-lock valve for automatic locking that allows easy, quick, and safe access to the interior of the bag through the connection of a needle-free syringe or a male vial adaptor.
Infusion port
Hermetic twist-off made of polypropylene for the connection of the infusion equipment. It maintains sterility until opened.
Delivery information
Grifols ships our 0.9% Sodium Chloride Fleboflex® Luer bags with a minimum order qualtity of a full sea container:
- Sea container (40 ft high cube reefer) contains: 46 EU pallets double-stacked
- EU pallet contains: 32 carton box (8 boxes per layer/4 layers)
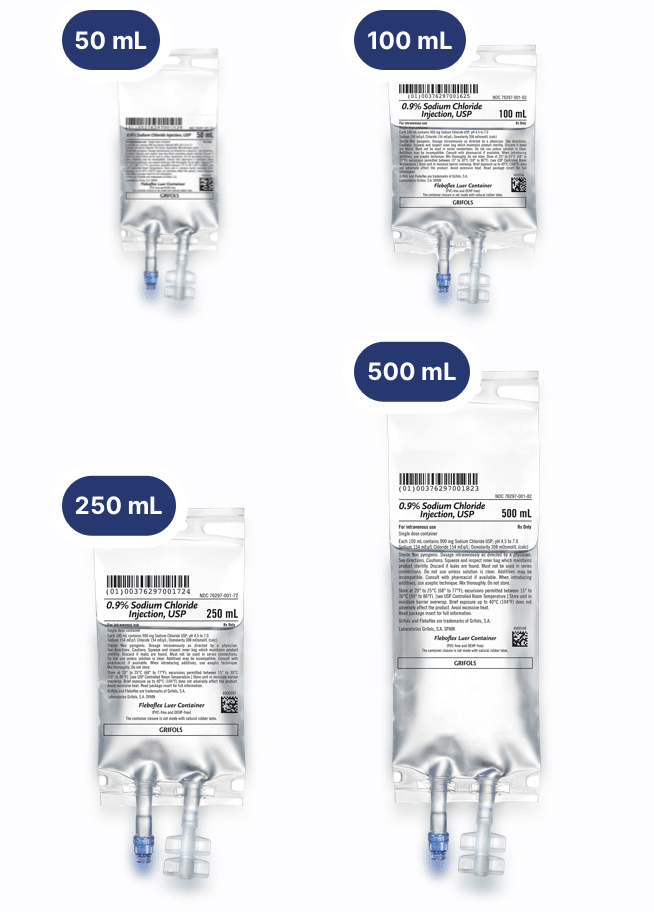
0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP 50/100 mL
- NDC Number
-
76297-001-51
- Case weight Kg
-
9
- Bags/ box
-
90
- Bags/ pallet
-
2880
- Bags/ container*
-
132,480
0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP 100/250 mL
- NDC Number
-
76297-001-61
- Case weight Kg
-
12
- Bags/ box
-
50
- Bags/ pallet
-
1600
- Bags/ container*
-
73,600
0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP 250/500 mL
- NDC Number
-
76297-001-71
- Case weight Kg
-
15
- Bags/ box
-
32
- Bags/ pallet
-
1024
- Bags/ container*
-
47,104
0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP 500/1000 mL
- NDC Number
-
76297-001-81
- Case weight Kg
-
19
- Bags/ box
-
24
- Bags/ pallet
-
768
- Bags/ container*
-
35,328
| Description | NDC Number | Case weight Kg | Bags/ box | Bags/ pallet | Bags/ container* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP 50/100 mL |
76297-001-51 |
9 |
90 |
2880 |
132,480 |
|
0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP 100/250 mL |
76297-001-61 |
12 |
50 |
1600 |
73,600 |
|
0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP 250/500 mL |
76297-001-71 |
15 |
32 |
1024 |
47,104 |
|
0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP 500/1000 mL |
76297-001-81 |
19 |
24 |
768 |
35,328 |
Guidelines for use of 0.9% Sodium Chloride solution in Fleboflex® Luer container
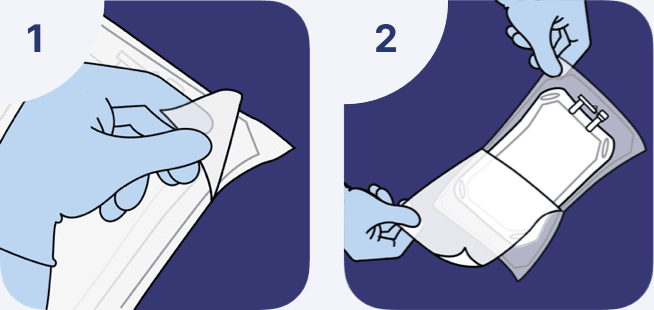
Overwrap removal
- The overwrap is designed to be opened by pulling apart the 2 sheets of the overwrap.
- The recommended method to remove the overwrap is to peel off one sheet by the corner while holding the other sheet at one end to carefully remove the solution container.
The overwrap should not be removed until product is to be used.
Container inspection
- Visually inspect the container for particulate matter and discoloration
- Check for minute leaks by squeezing the inner container firmly. If leaks are found, discard the solution as sterility may be impaired
- If the ports are damaged, detached, or not present, discard the container as solution path sterility may be impaired
- Do not administer unless the solution is clear and the seal is intact
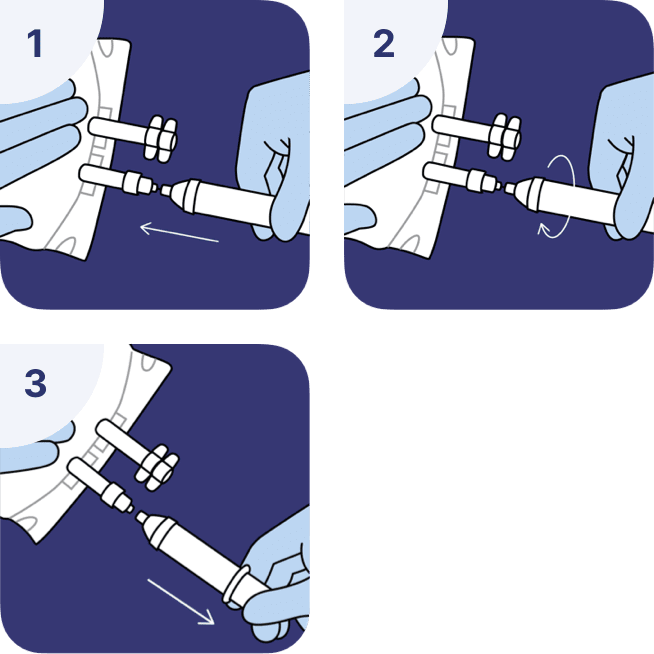
Adding medications and solution removal with a needle-free syringe
- Connect a syringe to the luer valve.
- Secure the connection with a small rotational movement.
- Add or remove solution.
The compatibility of the additives with Sodium Chloride 0.9% must be checked before adding a medication.
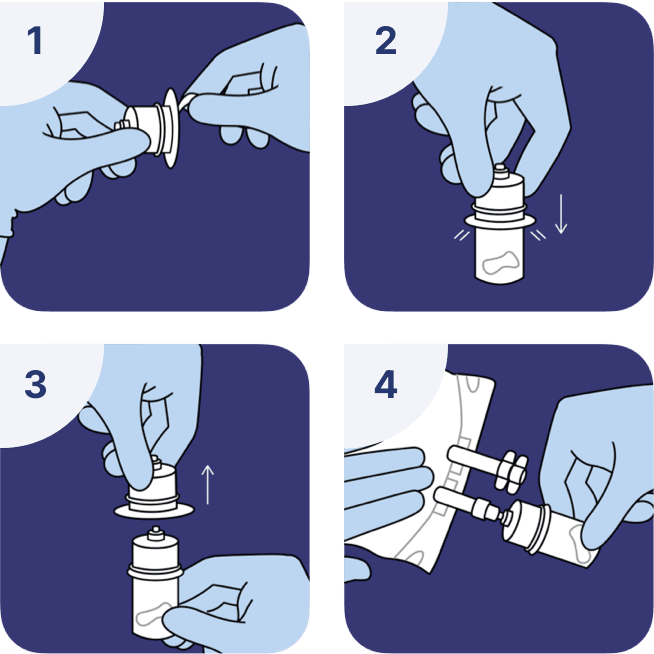
Reconstitution of vials with a vial adaptor
- Remove the protective foil from the blister containing the vial adaptor. Do not remove the adaptor from the blister.
- Without removing the blister, connect the vial adaptor to the vial by pressing vertically on the surface until the adaptor is fixed and the awl has penetrated the surface of the vial.
- Remove the blister.
- The vial with the vial adaptor is ready to reconstitute once connected to the luer valve of the bag.
Important Safety Information
Sodium Chloride Injection, USP is indicated as a source of water and electrolytes. 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP is also indicated for use as a priming solution in hemodialysis procedures.
Warnings
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity and infusion reactions, including hypotension, pyrexia, tremor, chills, urticaria, rash, and pruritus have been reported with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
Stop the infusion immediately if signs or symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction develop, such as tachycardia, chest pain, dyspnea and flushing. Appropriate therapeutic countermeasures must be instituted as clinically indicated.
Electrolyte Imbalances
Fluid Overload
Depending on the volume and rate of infusion, and the patient’s underlying clinical condition, the intravenous administration of Sodium Chloride Injection, USP can cause fluid disturbances such as overhydration/hypervolemia and congested states, including pulmonary congestion and edema.
Avoid 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP in patients with or at risk for fluid and/or solute overloading. If use cannot be avoided, monitor fluid balance, electrolyte concentrations, and acid base balance, as needed and especially during prolonged use.
Hyponatremia
Sodium Chloride Injection, USP may cause hyponatremia. Hyponatremia can lead to acute hyponatremic encephalopathy characterized by headache, nausea, seizures, lethargy, and vomiting. Patients with brain edema are at particular risk of severe, irreversible and lifethreatening brain injury. Avoid Sodium Chloride Injection, USP in patients with or at risk for hyponatremia. If use cannot be avoided, monitor serum sodium concentrations.
Hypernatremia
Hypernatremia may occur with Sodium Chloride Injection, USP. Conditions that may increase the risk of hypernatremia, fluid overload and edema (central and peripheral), include patients with: primary hyperaldosteronism; secondary hyperaldosteronism associated with, for example, hypertension, congestive heart failure, liver disease (including cirrhosis), renal disease (including renal artery stenosis, nephrosclerosis); and pre-eclampsia. Avoid Sodium Chloride Injection, USP in patients with, or at risk for, hypernatremia. If use cannot be avoided, monitor serum sodium concentrations.
Precautions
Patients with Severe Renal Impairment
Administration of Sodium Chloride Injection, USP in patients with or at risk of severe renal impairment, may result in hypernatremia and/or fluid overload. Avoid Sodium Chloride Injection, USP in patients with severe renal impairment or conditions that may cause sodium and/or potassium retention, fluid overload, or edema. If use cannot be avoided, monitor patients with severe renal impairment for development of these adverse reactions.
Drug Interactions
Other Products that Affect Fluid and/or Electrolyte Balance
Administration of Sodium Chloride Injection, USP to patients treated concomitantly with drugs associated with sodium and fluid retention may increase the risk of hypernatremia and volume overload. Avoid use of Sodium Chloride Injection, USP in patients receiving such products, such as corticosteroids or corticotropin. If use cannot be avoided, monitor serum electrolytes, fluid balance and acid-base balance.
Lithium
Renal sodium and lithium clearance may be increased during administration of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP. Monitor serum lithium concentrations during concomitant use.
Other Drugs that Increase the Risk of Hyponatremia
Administration of Sodium Chloride Injection, USP in patients treated concomitantly with medications associated with hyponatremia may increase the risk of developing hyponatremia.
Avoid use of Sodium Chloride Injection, USP in patients receiving products, such as diuretics, and certain antiepileptic and psychotropic medications. Drugs that increase the vasopressin effect reduce renal electrolyte free water excretion and may also increase the risk of hyponatremia following treatment with intravenous fluids. If use cannot be avoided, monitor serum sodium concentrations.
Pregnancy
Sodium Chloride Injection, USP should be given during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential
risk to the fetus.
Lactation
It is not known whether this drug is present in human milk. Because many drugs are present in human milk, caution should be exercised when Sodium Chloride Injection, USP is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Closely monitor plasma electrolyte concentrations in pediatric patients who may have impaired ability to regulate fluids and electrolytes. In very low birth weight infants, excessive or rapid administration of Sodium Chloride Injection, USP may result in increased serum osmolality and risk of intracerebral hemorrhage.
Children (including neonates and older children) are at increased risk of developing hyponatremia as well as for developing hyponatremic encephalopathy.
Geriatric Use
Geriatric patients are at increased risk of developing electrolyte imbalances. Sodium Chloride Injection, USP is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function.
Adverse Reactions
The following adverse reactions have been reported in the post-marketing experience during use of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP and include the following: General disorders and administration site conditions (Infusion site erythema, injection site streaking, burning sensation, and infusion site urticaria), Hypersensitvity reactions: (Hypotension, pyrexia, tremor, chills, urticaria, rash, and pruritus), Metabolism and nutrition disorders (Hypernatremia, hyponatremia, hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis) and Nervous System Disorders (Hyponatremic encephalopathy).
Do you have any questions or concerns?
Contact a Grifols representative for more information